Important: This article is for informational purposes only. Please read our full disclaimer for more details.
Your liver is one of the hardest-working organs in your body — detoxifying harmful substances, supporting digestion, and maintaining metabolic balance. Yet, it often goes unnoticed until problems arise. Thankfully, nature offers several herbs that can help nourish and protect your liver. From ancient Ayurvedic ingredients to modern herbal remedies, these natural allies can support liver function, repair damage, and promote overall vitality when used wisely.
In this guide, we’ll explore 10 of the best herbs for liver health, backed by traditional wisdom and scientific evidence — along with important precautions to keep in mind.
Top 10 Herbs to Support and Protect Liver Health
Your liver is the body’s primary detox organ — it filters toxins, regulates hormones, processes fats, and stores essential nutrients. Herbal medicine has long recognized the liver as the “seat of vitality,” and many traditional systems — including Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), and Western herbalism — have relied on natural botanicals to strengthen and protect this vital organ.
Below are ten of the best herbs known for their liver-supportive properties, their proven benefits, and precautions for safe use.
1. Milk Thistle (Silybum Marianum)
Why it works:
- Milk thistle is often referred to as the “liver’s best friend.” Its active component, silymarin, is a complex of flavonolignans that stabilizes liver cell membranes and stimulates protein synthesis, encouraging regeneration of damaged liver tissue.
Scientific insight:
- A review in the Journal of Hepatology found that silymarin reduced oxidative stress and improved liver enzyme markers in people with liver disease (1). It’s also used as a supportive treatment in cases of cirrhosis, hepatitis, and fatty liver disease.
How to use: Milk thistle supplements or teas are most common. Typical dosage: 200–400 mg silymarin daily.
Precaution: Avoid if you’re allergic to ragweed or similar plants. It can interact with medications processed by the liver.
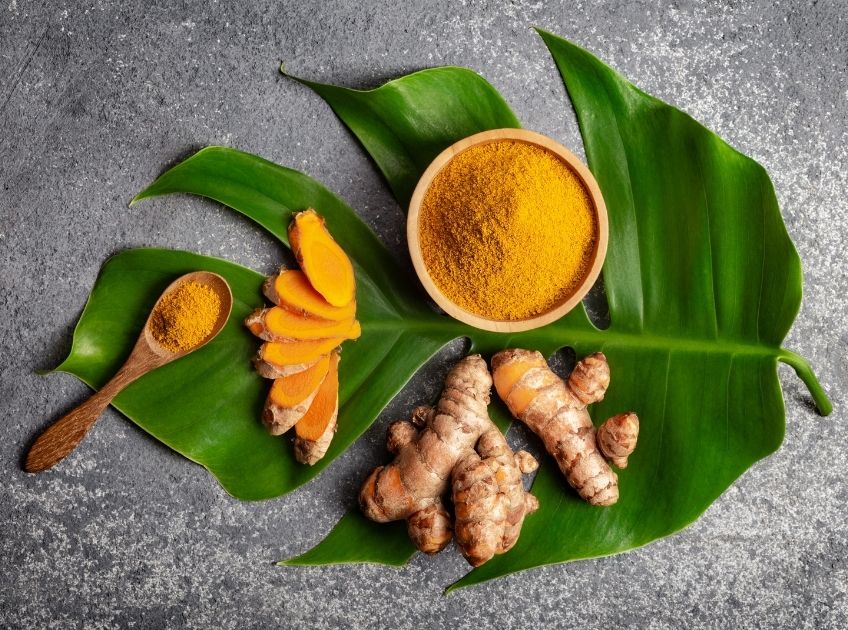
2. Turmeric (Curcuma Longa)
Why it works:
- This golden spice has been a cornerstone of Ayurvedic healing for thousands of years. Its active compound, curcumin, combats inflammation and neutralizes free radicals that can damage liver cells.
Scientific insight:
- Studies in the World Journal of Gastroenterology found that curcumin supplementation reduced liver fat accumulation and improved enzyme balance in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (2).
How to use: Add turmeric to curries, soups, or drink it as golden milk. For supplements, look for formulations combined with black pepper (piperine) to boost absorption.
Precaution: High doses may cause nausea or interfere with blood thinners.
3. Dandelion Root (Taraxacum Officinale)
Why it works:
- Once dismissed as a garden weed, dandelion root is a natural diuretic and bile stimulant, helping the liver flush out toxins more efficiently.
Scientific insight:
- Animal studies published in Food and Chemical Toxicology suggest that dandelion extract may prevent alcohol-induced liver injury and oxidative damage (3).
How to use: Enjoy as a tea made from dried roots or take as a tincture or capsule.
Precaution: Avoid if you have gallstones or bile duct obstruction.
4. Licorice Root (Glycyrrhiza Glabra)
Why it works:
- Licorice has been used in both Eastern and Western medicine to soothe and heal the liver. Its compound glycyrrhizin helps reduce inflammation and protect against liver toxins.
Scientific insight:
- Clinical trials have found that glycyrrhizin may improve liver function in patients with chronic hepatitis and lower ALT and AST enzyme levels (4).
How to use: Often taken as a tea or in capsule form (deglycyrrhizinated versions are gentler for long-term use).
Precaution: Prolonged or high-dose use can lead to elevated blood pressure or potassium loss.
5. Schisandra Berry (Schisandra Chinensis)
Why it works:
- Known in TCM as a “five-flavor fruit,” schisandra helps the liver adapt to stress and enhances its detoxification capacity by increasing enzyme activity.
Scientific insight:
- Research in the American Journal of Chinese Medicine shows that schisandra extracts may improve liver enzyme balance and help in managing hepatitis (5).
How to use: Commonly available in powder, capsule, or tincture form. Often used in combination with goji berries or ginseng in tonic blends.
Precaution: Avoid during pregnancy or when taking sedatives.
6. Artichoke Leaf (Cynara Scolymus)
Why it works:
- Artichoke leaf supports bile production, aiding fat digestion and detoxification. It’s also believed to help regenerate liver tissue.
Scientific insight:
- A 2018 study in Phytomedicine found that artichoke extract significantly improved liver enzyme levels and reduced symptoms of indigestion (6).
How to use: It can be taken as an extract, capsule, or brewed tea made from dried leaves.
Precaution: Avoid if allergic to daisies, marigolds, or chrysanthemums.
7. Ginger (Zingiber Officinale)
Why it works:
- Ginger promotes circulation and supports detox pathways, helping the liver process fats and toxins more effectively.
Scientific insight:
- A 2020 study in Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine demonstrated that ginger supplementation improved liver enzymes and reduced inflammation in NAFLD patients (7).
How to use: Drink ginger tea daily or add fresh ginger to meals and smoothies.
Precaution: Large doses may interact with anticoagulant drugs or cause mild stomach irritation.
8. Holy Basil (Ocimum Sanctum/Tulsi)
Why it works:
- A sacred herb in Ayurveda, tulsi is an adaptogen that helps the body resist stress. It protects liver cells from damage caused by pollutants and heavy metals.
Scientific insight:
- Studies have found tulsi extracts to be hepatoprotective, reducing liver toxicity caused by drugs and industrial chemicals (8).
How to use: Enjoy fresh tulsi leaves as tea, or take in capsule or tincture form.
Precaution: May lower blood sugar levels — use with caution if diabetic.
9. Burdock Root (Arctium Lappa)
Why it works:
- Traditionally used as a blood purifier, burdock root enhances liver function by increasing bile flow and filtering impurities from the bloodstream.
Scientific insight:
- Research in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology shows burdock extract possesses powerful antioxidant effects that help protect liver cells from toxins (9).
How to use: Drink as tea, or add cooked burdock root to soups and stews.
Precaution: Avoid during pregnancy or if taking diuretics, as it may amplify their effects.
10. Green Tea (Camellia Sinensis)
Why it works:
- Green tea is rich in catechins — especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) — which support liver detoxification and fat metabolism.
Scientific insight:
- A review in the World Journal of Gastroenterology found that green tea improves liver enzyme levels and helps reduce liver fat accumulation in NAFLD patients (10).
How to use: Drink 2–3 cups daily for best results, or take standardized green tea extract under professional supervision.
Precaution: Avoid excessive intake of green tea extracts, as very high doses may stress the liver.
How These Herbs Work Together?
Collectively, these herbs:
- Enhance detoxification (Milk thistle, dandelion, artichoke)
- Reduce inflammation (Turmeric, ginger, licorice)
- Improve bile production (Dandelion, artichoke, burdock)
- Regenerate liver cells (Milk thistle, schisandra)
- Protect against oxidative stress (Green tea, holy basil)
When used responsibly, these botanicals can work synergistically to maintain liver resilience and vitality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’S)
1. Can I take multiple liver-supporting herbs together?
A. It’s best to use one or two herbs at a time under professional guidance to prevent potential interactions and ensure proper dosage.
2. How long does it take for herbal liver tonics to show results?
A. Typically, noticeable effects may take 4–8 weeks of consistent use, but results vary depending on diet, lifestyle, and liver condition.
3. Are herbal supplements safe for people with liver disease?
A. Some herbs can be beneficial, while others may worsen liver issues. Always seek medical advice before taking any supplements if you have liver concerns.
Herbs can be powerful allies in maintaining liver health — but they work best alongside a balanced diet, hydration, and limiting alcohol and processed foods. Think of these herbs as gentle supporters rather than magic cures. With mindful use and expert guidance, natural remedies like milk thistle, turmeric, and dandelion can help your liver perform at its best for years to come.