Important: This article is for informational purposes only. Please read our full disclaimer for more details.
Skin hyperpigmentation—whether it appears as sunspots, melasma, or post-inflammatory marks—happens when your skin produces excess melanin. While dermatological treatments such as chemical peels, retinoids, and laser therapy are effective, many people prefer starting with natural, low-irritation remedies at home.
Several botanicals and kitchen ingredients contain bioactive compounds that can help brighten skin, support cell turnover, and reduce pigment buildup. Below, you’ll find expert-curated natural options backed by scientific understanding of how these ingredients work.
6 Natural Remedies That May Help Fade Hyperpigmentation
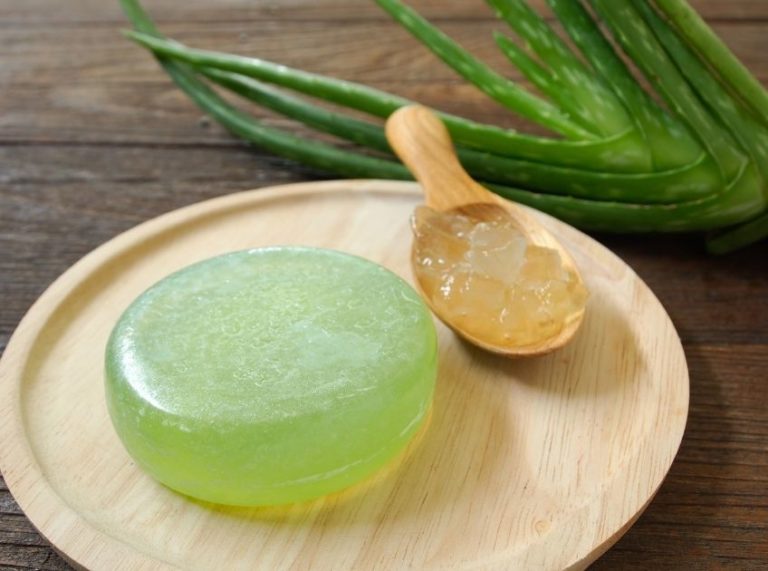
1. Aloe Vera Gel: Supports Melanin Breakdown and Calms Inflammation
Aloe vera is more than a soothing hydrator—it contains aloin and aloesin, two compounds shown in laboratory studies to help reduce melanin production (1). Aloesin, in particular, may interrupt the process that leads to dark spots by inhibiting tyrosinase activity.
Why it may help:
- Reduces melanin formation over time
- Helps lighten UV-induced pigmentation
- Hydrates and repairs skin, which supports the healing of acne marks
How to use effectively:
- Apply fresh aloe gel or a 99% pure store-bought gel at night
- Rinse off in the morning
- Use daily for at least 6–8 weeks for best results
Best for: Early-stage dark spots, sunspots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation on sensitive skin.
2. Green Tea Extract: Antioxidant Defense Against Pigment Formation
Green tea is rich in epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), an antioxidant that may help reduce oxidative stress—one of the triggers of hyperpigmentation. Some studies suggest EGCG can also influence melanin synthesis pathways, making it a gentle but effective brightening ingredient (2).
Why it may help:
- Reduces inflammation that contributes to pigmentation
- Limits free-radical damage from sun exposure
- Helps prevent deepening of existing spots
How to use effectively:
- Brew green tea, allow it to cool, and apply with a cotton pad twice daily
- OR choose serums containing 2–5% green tea extract
- Use consistently for several weeks
Best for: People with inflamed skin, sun-induced pigmentation, and acne-prone skin.
3. Licorice Root Extract: A Potent Natural Brightener with Glabridin
Licorice root is a dermatologist-favorite natural brightener because of glabridin, a compound known for inhibiting tyrosinase without irritating the skin. It also helps calm redness and inflammation, which is especially beneficial for pigmentation caused by acne.
Why it may help:
- Reduces melanin production
- Helps fade stubborn dark spots
- Calms redness that often accompanies pigmentation
How to use effectively:
- Apply a licorice-infused serum or gel once or twice daily
- Spot treat darker areas for targeted brightening
- Combine with aloe or niacinamide for faster results
Best for: Melasma, acne marks, and sunspots. Safe for sensitive or reactive skin.
4. Turmeric Paste: Curcumin for Powerful Antioxidant and Anti-Melanogenic Activity
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound widely studied for its ability to regulate melanin production and combat skin inflammation (3). It also has antioxidant properties that help prevent pigment darkening.
Why it may help:
- Helps interrupt melanin synthesis
- Reduces inflammation that deepens pigmentation
- May help brighten overall skin tone
How to use effectively:
- Mix 1 teaspoon of turmeric with yogurt, aloe, or honey
- Apply as a face mask for 10–15 minutes, 2–3 times weekly
- Rinse well to avoid staining
Best for: Stubborn pigmentation, dull skin, and uneven tone—especially in oily or combination skin types.
5. Apple Cider Vinegar: Natural Exfoliation and Spot Lightening
Apple cider vinegar contains acetic acid, which may help lighten pigmentation by promoting gentle exfoliation and regulating the skin’s pH. It can remove dead skin cells and reveal brighter, more even skin underneath.
Why it may help:
- Encourages mild exfoliation
- Helps lighten surface-level pigmentation
- Improves skin texture over time
How to use effectively:
- Always dilute: 1 part ACV to 3 parts water
- Apply with a cotton pad to pigmented areas for 5–10 minutes
- Rinse off and moisturize
- Start 2–3 times weekly to avoid irritation
Best for: Mild sunspots and surface-level pigmentation. Not recommended for very sensitive skin.
6. Rosehip Oil: Vitamin-Rich Support for Skin Regeneration
Rosehip oil contains natural vitamin A derivatives, vitamin C, and essential fatty acids that support cell turnover and skin repair. These qualities help fade dark spots and improve the skin’s overall clarity.
Why it may help:
- Increases skin renewal rate
- Fades older dark spots over time
- Supports the healing of acne marks
- Provides deep nourishment without clogging pores
How to use effectively:
- Apply 2–3 drops to clean skin at night
- Use alone or mix with your moisturizer
- Noticeable improvements typically appear after 8–12 weeks
Best for: Dry, mature, or scar-prone skin with lingering pigmentation.
Why These Natural Ingredients Work?
- Melanin production is influenced by enzymes (particularly tyrosinase), inflammation, and oxidative stress.
- Most natural brightening agents work by:
- inhibiting tyrosinase (licorice, aloe vera, turmeric)
- reducing inflammation linked to pigment formation (green tea, aloe, rosehip)
- promoting gentle exfoliation or cell turnover (apple cider vinegar, rosehip oil)
While results from natural remedies are gradual, consistency and sun protection can significantly enhance their effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’S)
1. How long do natural treatments take to fade hyperpigmentation?
A. Most people begin to notice subtle improvements within 4–8 weeks, but stubborn pigmentation—especially melasma—may take several months to resolve. Patience and consistency are key.
2. Can I combine multiple natural remedies?
A. Yes, but introduce one remedy at a time. This helps avoid irritation and allows you to observe which ingredient works best for your skin.
3. Are natural remedies safe for all skin types?
A. Generally, yes. However, sensitive skin may react to acidic ingredients like ACV or turmeric. Always perform a patch test and discontinue use if irritation occurs.
Natural remedies can be a gentle, affordable, and effective way to reduce skin hyperpigmentation when used consistently and paired with daily sun protection. Ingredients like aloe vera, licorice, green tea, and rosehip oil offer science-supported benefits that help regulate melanin production and support healthy skin renewal.
Start slowly, listen to your skin, and choose remedies that fit your routine—your complexion will gradually become brighter, clearer, and more even-toned.















