Important: This article is for informational purposes only. Please read our full disclaimer for more details.
Quality sleep is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity many people struggle to get. Stress, digital overload, hormonal imbalance, chronic pain, and lifestyle patterns all interfere with the body’s ability to fall asleep and stay asleep. This is where natural sleep aids come in. Unlike prescription sleep medications, which may cause dependency or next-day grogginess, natural remedies often work with your body’s biological rhythms to restore balance and optimize rest.
In this guide, we dive into nine of the most effective natural sleep aids, how they work, how to use them, and what science says about their benefits.
Nature’s Nighttime Helpers: 9 Best Natural Sleep Aids
1. Melatonin – The Body’s Sleep Hormone
Melatonin is a hormone your pineal gland naturally produces in response to darkness. It signals your brain that it’s time to sleep.
How it works: Melatonin regulates circadian rhythms—the internal clock that governs sleep–wake cycles.
Scientific Evidence: A meta-analysis published in Sleep Medicine Reviews found that melatonin supplementation can shorten sleep onset time and improve overall sleep quality, especially for people with insomnia or jet lag (1).
How to use:
- 0.5–5 mg, 30–60 minutes before bed
- Start with the lowest dose to assess tolerance
2. Magnesium – The Relaxation Mineral
Magnesium plays a central role in muscle relaxation, nerve function, and stress regulation.
How it works: It supports GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) activity—a calming neurotransmitter that quiets the nervous system.
Scientific Evidence: A randomized clinical trial in the Journal of Research in Medical Sciences found that magnesium supplementation significantly improved sleep time, sleep efficiency, and reduced early morning awakening (2).
How to use:
- 200–400 mg magnesium glycinate or magnesium citrate before bed
- Avoid magnesium oxide (poor absorption)
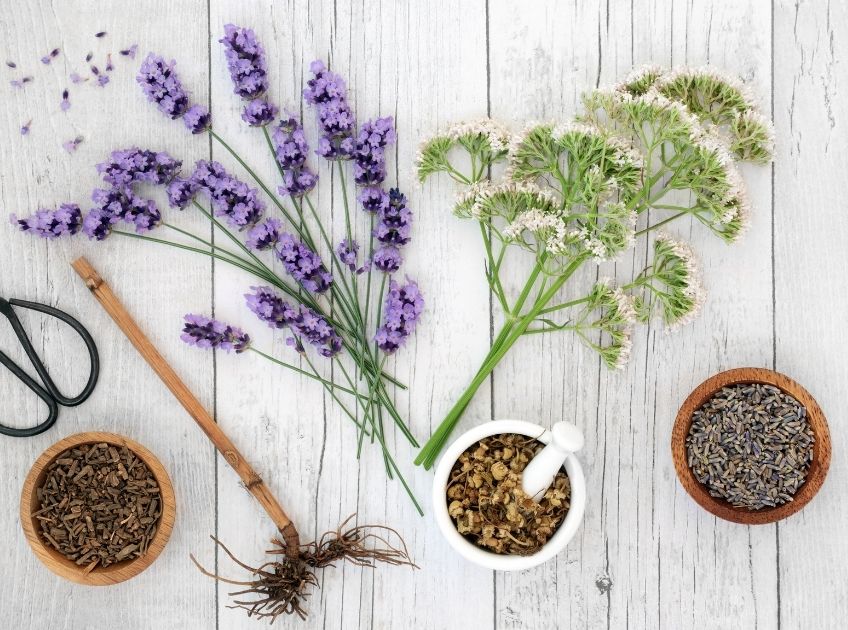
3. Valerian Root – The Herbal Sedative
Often called “nature’s Valium,” valerian root has been used for centuries as a calming herb.
How it works: It increases GABA availability, helping the brain settle into a relaxed state.
Scientific Evidence: A study in Phytomedicine reported that valerian root improved sleep latency and sleep quality in adults with mild insomnia (3).
How to use:
- 300–600 mg extract, 30 minutes before bedtime
- Can be taken as a tea, capsule, or tincture
4. Chamomile – The Soothing Bedtime Classic
Chamomile is widely known for its calming aroma and naturally occurring antioxidants.
How it works: Apigenin, a flavonoid in chamomile, binds to benzodiazepine receptors in the brain—promoting sedation.
Scientific Evidence: Research in the Journal of Advanced Nursing found that chamomile significantly improved sleep quality in postpartum women (4).
How to use:
- 1–2 cups of chamomile tea before bed
- Chamomile extract (200–400 mg)
5. Lavender – Aromatherapy That Works
Lavender is frequently used in sleep sprays, oils, and diffusers for its strong calming effects.
How it works: The scent targets the limbic system—the emotional center of the brain—reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
Scientific Evidence: A study published in Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found lavender aromatherapy significantly improved sleep quality in college students (5).
How to use:
- Essential oil diffuser
- Pillow spray
- 80–160 mg lavender extract (capsule)
6. L-Theanine – Calm Without Drowsiness
An amino acid commonly found in green tea, L-theanine, promotes relaxation without sedation.
How it works: It increases alpha brain waves—associated with calm mental focus—while reducing cortisol.
Scientific Evidence: A study in Nutrients showed that L-theanine improved sleep latency, reduced stress, and supported deeper sleep (6).
How to use:
- 100–400 mg 30 minutes before sleep
- Often paired with magnesium or GABA supplements
7. Passionflower – For a Quiet, Calm Mind
Passionflower is known for easing restlessness and racing thoughts.
How it works: It enhances GABA levels and supports the parasympathetic nervous system.
Scientific Evidence: A study in Phytotherapy Research found that passionflower tea improved subjective sleep quality after just one week of use (7).
How to use:
- 1 cup of passionflower tea before bed
- 200–500 mg extract
8. Glycine – A Sleep-Promoting Amino Acid
Glycine is a simple amino acid with surprising benefits for sleep.
How it works: It lowers core body temperature—a signal for the body to initiate sleep.
Scientific Evidence: Research in Sleep and Biological Rhythms reported that glycine improved sleep quality and reduced next-day fatigue (8).
How to use:
- 3 grams of powder mixed in water before bed
- Often combined with magnesium
9. Tart Cherry Juice – A Natural Source of Melatonin
Tart cherries contain natural melatonin and antioxidants.
How it works: Supports melatonin production and reduces oxidative stress that interferes with sleep.
Scientific Evidence: A study in the American Journal of Therapeutics found that tart cherry juice improved sleep duration and efficiency in adults with insomnia (9).
How to use:
- 1 cup tart cherry juice 1–2 hours before bed
- Avoid juices with added sugar
Science Spotlight: What Research Really Says
Natural sleep aids can support:
- Faster sleep onset
- Reduced nighttime awakenings
- Better REM and deep sleep cycles
- Lower stress, anxiety, and nervous system stimulation
However, results vary by individual, dosage, and underlying health factors. These remedies work best when paired with good sleep hygiene—consistent bedtime routines, reduced blue light, and stress management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’S)
1. Are natural sleep aids safe to use long-term?
A. Most are generally safe when taken in recommended doses. However, herbs like valerian and passionflower should be used cautiously if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking other medications. Always check with a healthcare provider for long-term use.
2. Can I combine multiple natural sleep aids?
A. Yes—many people use combinations such as melatonin + magnesium or L-theanine + chamomile. Avoid mixing too many sedative herbs without medical advice.
3. How soon will I notice results?
A. Some aids (like melatonin or lavender) work within an hour, while others (like magnesium or valerian) may take several days to show full effects.
Natural sleep aids offer a gentle yet effective way to support your sleep cycle without the harsh side effects of prescription sedatives. Whether you prefer herbs, amino acids, or nutrient-based supplements, consistency is key. Start with one remedy, monitor your body’s response, and let science guide your choices.
If sleep has been hard to come by, these nine natural aids—each backed by research—can help you create a calm, restful nighttime routine that supports total well-being.