Important: This article is for informational purposes only. Please read our full disclaimer for more details.
Feeling overwhelmed, restless, or constantly on edge? You’re not alone. Stress and anxiety have become increasingly common in today’s fast-paced world. While therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes play a role, one of the simplest yet most powerful tools for calming the mind and body is something we do every day — breathing.
Conscious breathing techniques help regulate your nervous system, lower stress hormones, and promote emotional balance. In this guide, we’ll explore effective breathing practices, the science behind how they work, and practical tips to help you manage stress and anxiety naturally.
How Breathwork Helps Reduce Stress and Anxiety
When we’re anxious, our breathing often becomes shallow and rapid, triggering the body’s “fight-or-flight” response. This keeps stress hormones like cortisol elevated and can make anxiety worse. Breathing practices work by:
- Activating the parasympathetic nervous system → calming the body and reducing heart rate
- Lowering cortisol levels → reducing the physical effects of stress
- Improving oxygen flow → enhancing brain function and emotional regulation
- Releasing physical tension → easing tightness in the chest, shoulders, and diaphragm
A study published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience (2021) found that slow, controlled breathing significantly improves emotional regulation and reduces anxiety symptoms by directly influencing the brain’s stress-response mechanisms (1)(2).
5 Effective Breathing Practices to Calm Stress and Anxiety
These scientifically supported techniques are simple, quick, and effective. You can do them anytime — whether you’re at work, in bed, or commuting.
1. Diaphragmatic Breathing (Belly Breathing)
Purpose: Calms the nervous system and reduces tension.
How to do it
- Sit or lie down comfortably and place one hand on your belly.
- Inhale deeply through your nose, letting your belly rise.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth, letting your belly fall.
- Repeat for 5–10 minutes.
Why it works: Studies show that diaphragmatic breathing activates the vagus nerve, which lowers heart rate and promotes relaxation.
2. Box Breathing
Purpose: Balances oxygen levels and brings mental clarity.
How to do it
- Inhale through your nose for 4 counts.
- Hold your breath for 4 counts.
- Exhale slowly for 4 counts.
- Pause for 4 counts before the next inhale.
- Repeat for 5 rounds.
Why it works: Popular among Navy SEALs, box breathing stabilizes the nervous system and reduces both emotional and physical stress responses.
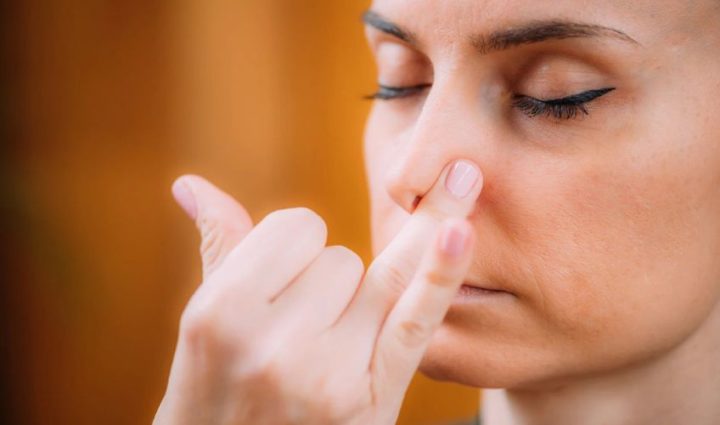
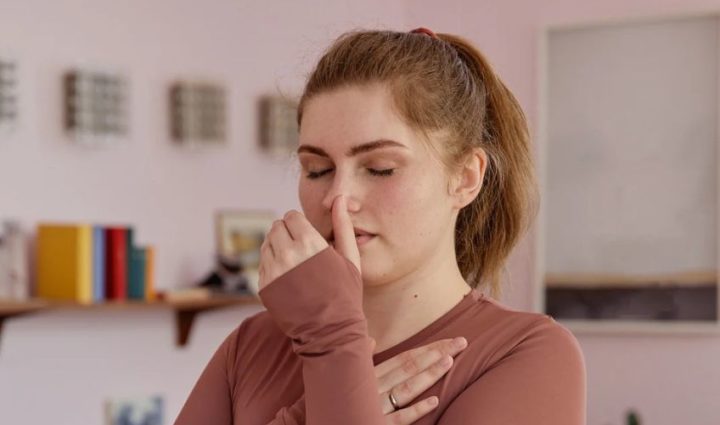
3. Alternate Nostril Breathing (Nadi Shodhana)
Purpose: Balances energy, reduces anxiety, and improves focus.
How to do it
- Sit upright and relax your shoulders.
- Close your right nostril with your thumb and inhale through your left nostril.
- Close your left nostril with your ring finger and exhale through your right nostril.
- Inhale through the right nostril, close it, and exhale through the left.
- Continue for 5 minutes.
Why it works: Research in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine shows that this technique reduces heart rate variability and promotes mental calmness (3).
4. 4-7-8 Breathing Technique
Purpose: Eases anxiety and promotes better sleep.
How to do it
- Inhale deeply through your nose for 4 counts.
- Hold your breath for 7 counts.
- Exhale completely through your mouth for 8 counts.
- Repeat for 4–6 cycles.
Why it works: Developed by Dr. Andrew Weil, this method slows down the heart rate, activates the parasympathetic system, and helps quiet racing thoughts (4).
5. Resonance Breathing (Coherent Breathing)
Purpose: Synchronizes breathing and heart rhythms for deep relaxation.
How to do it
- Sit comfortably and close your eyes.
- Inhale through your nose for 5.5 seconds.
- Exhale through your nose for 5.5 seconds.
- Continue for 10 minutes.
Why it works: A study published in Frontiers in Psychology found that resonance breathing optimizes heart rate variability and reduces anxiety significantly (5).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’S)
1. How long should I practice breathing techniques daily?
A. Just 5–15 minutes a day can make a noticeable difference in reducing stress and anxiety.
2. Can breathwork replace anxiety medication?
A. Breathing exercises are a powerful complementary tool, but they shouldn’t replace professional medical advice or treatment. Always consult a healthcare provider if anxiety persists.
3. When is the best time to practice these techniques?
A. Morning sessions can set a calm tone for the day, while evening practice can improve sleep quality. You can also use them anytime anxiety strikes.
Breathing practices are a simple, natural, and effective way to manage stress and anxiety. By incorporating techniques like diaphragmatic breathing, box breathing, and alternate nostril breathing into your daily routine, you can retrain your nervous system and achieve a sense of calm and balance.