Important: This article is for informational purposes only. Please read our full disclaimer for more details.
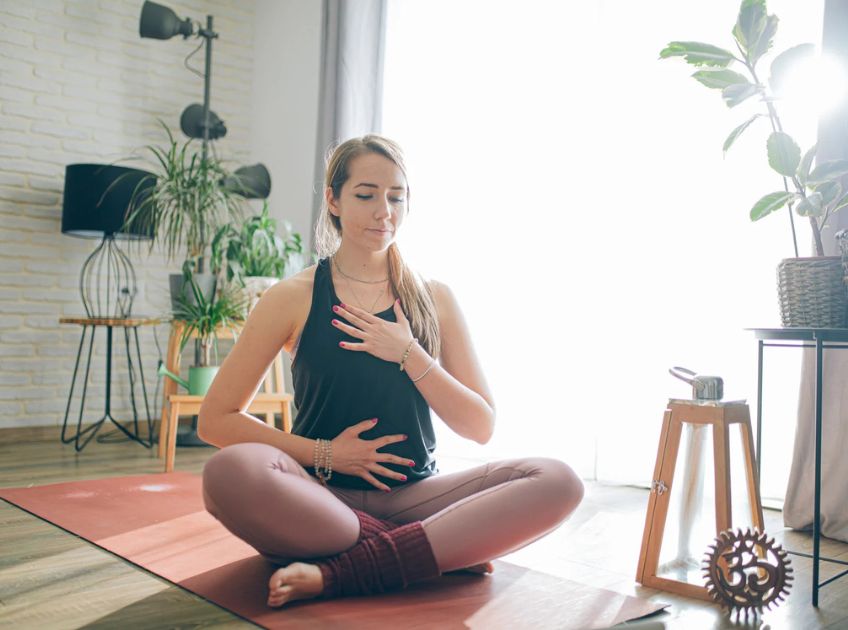
Anxiety doesn’t just live in your mind — it often manifests physically. Racing heartbeats, tense shoulders, shallow breathing, and a knot in your stomach are all signs that your body is holding onto stress. Traditional talk therapies primarily address thoughts and emotions, but what about the body’s role in anxiety?
This is where somatic therapy comes in. Rooted in the idea that trauma and anxiety are stored within the body, somatic therapy uses mind-body awareness, gentle movements, breathwork, and grounding techniques to help release stored tension and restore balance.
In this article, we’ll explore how somatic therapy works, its scientific backing, effective techniques for anxiety relief, and why it may be a powerful complement to conventional therapy.
Key Insights: Somatic Techniques and Anxiety Management
Somatic therapy focuses on reconnecting with bodily sensations to manage anxiety. Here are the main takeaways:
- Anxiety often triggers fight-or-flight responses in the body, even without immediate danger.
- Somatic therapy uses breathing, movement, and mindfulness to help regulate these responses.
- Research suggests somatic practices can lower cortisol levels and reduce anxiety symptoms.
- It promotes emotional regulation by teaching you to recognize and release stored tension.
- Somatic techniques complement other therapies like CBT and mindfulness-based stress reduction.
How Somatic Experiencing Works for Anxiety Relief
Developed by Dr. Peter A. Levine, Somatic Experiencing (SE) is one of the most widely practiced somatic therapies. SE works by gently guiding individuals to notice physical sensations linked to anxiety and complete the body’s stress cycles (1).
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
- Tracking Sensations – You learn to observe subtle bodily cues like muscle tension, heartbeat, and breath patterns.
- Titration – Instead of diving straight into anxiety-inducing memories, SE introduces them gradually to prevent overwhelm.
- Pendulation – You move back and forth between sensations of discomfort and safety, teaching the nervous system to self-regulate.
- Completion – The body releases stored fight-or-flight energy through subtle tremors, sighs, or deep relaxation.
Scientific evidence
A 2017 study published in the Journal of Traumatic Stress found that Somatic Experiencing significantly reduced anxiety and PTSD symptoms, especially in individuals who experienced chronic stress (2)(3).
Benefits of Somatic Therapy for Anxiety
| Benefit | How It Helps with Anxiety |
|---|---|
| Improved Nervous System Regulation | Reduces fight-or-flight activation and promotes calmness. |
| Enhanced Emotional Awareness | Helps you identify and process emotions stored in the body. |
| Reduced Physical Symptoms | Relieves muscle tension, shallow breathing, and fatigue caused by anxiety. |
| Lower Cortisol Levels | Some studies show somatic therapy can reduce stress hormones. |
| Trauma Healing | Resolves underlying trauma that often fuels anxiety disorders. |
| Better Mind-Body Connection | Promotes awareness and control over physical stress responses. |
5 Somatic Techniques to Soothe Anxiety
Somatic techniques are designed to calm your nervous system, release stored tension, and retrain your body to respond differently to stress. Below are five highly effective techniques explained in depth:
1. Grounding Through Body Scanning
Anxiety often pulls you into future-oriented worries or racing thoughts. Body scanning is a mindfulness-based somatic technique that gently anchors your awareness in the present moment.
How to Do It
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable position.
- Close your eyes and take three deep breaths to center yourself.
- Start by focusing on your feet. Notice sensations — warmth, tingling, or even numbness.
- Gradually move your attention upward: calves, thighs, hips, abdomen, chest, shoulders, arms, and finally, your head.
- If you find tension, breathe into that area and visualize relaxation flowing there.
Why It Works
- Brings awareness away from anxious thoughts and into the body’s present sensations.
- Research in the Journal of Anxiety Disorders suggests body scanning can reduce physiological arousal associated with anxiety (4).
- Over time, it rewires the brain to stay more grounded in moments of stress.
2. Diaphragmatic Breathing to Reset the Nervous System
When anxiety hits, your breathing becomes shallow and rapid, signaling your body to stay in fight-or-flight mode. Diaphragmatic breathing — also called belly breathing — flips the switch, activating the parasympathetic nervous system (your natural “rest-and-digest” mode).
How to Do It
- Sit comfortably or lie flat on your back.
- Place one hand on your chest and the other on your belly.
- Inhale slowly through your nose for 4 seconds, allowing your belly to rise.
- Hold your breath for 2 seconds.
- Exhale deeply through your mouth for 6 seconds, letting your belly fall.
- Repeat for 5–10 minutes daily or during anxious moments.
Why It Works
- Reduces cortisol levels and slows the heart rate.
- A 2020 study in Frontiers in Psychology found diaphragmatic breathing improves emotional regulation and reduces anxiety symptoms (5).
- With regular practice, it trains your nervous system to return to calm faster.
3. Orienting Technique to Bring Safety Signals to the Brain
Anxiety can make your body hyper-vigilant, keeping you stuck in a loop of perceived danger. The orienting technique reassures your nervous system by showing it that your current environment is safe.
How to Do It
- Sit comfortably and look around the room slowly.
- Identify five objects you can see — name them out loud if you want.
- Touch three nearby surfaces and describe their textures (e.g., “smooth,” “soft,” “cool”).
- Listen carefully and notice three different sounds around you.
- Finally, take a deep breath and feel the weight of your body against the chair or floor.
Why It Works
- Activates the parasympathetic nervous system, signaling safety.
- Helps break the “thought spiral” caused by anxiety.
- Used in Somatic Experiencing therapy to restore a sense of groundedness and control.
4. Pendulation: Releasing Trapped Stress Responses
When anxiety stems from unresolved past experiences or trauma, the body may hold on to fight-or-flight energy. Pendulation is a somatic technique where you gently shift between areas of tension and ease, teaching your nervous system how to self-regulate.
How to Do It
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable, quiet space.
- Bring attention to a part of your body where you feel anxiety physically — maybe tightness in the chest or knots in the stomach.
- Stay there for a few seconds, just noticing sensations without judgment.
- Now, shift your awareness to a body part that feels neutral or comfortable — perhaps your hands or feet.
- Slowly move your attention back and forth between the two areas.
- Continue for 5 minutes until you feel a subtle release or softening in the tension.
Why It Works
- Teaches your body that it’s safe to experience mild discomfort without being overwhelmed.
- A study in the European Journal of Psychotraumatology found that pendulation reduces stress reactivity and promotes emotional resilience (6).
- Encourages your nervous system to complete unfinished stress cycles.
5. Gentle Movement and Stretching to Release Stored Energy
Anxiety often causes muscle stiffness, especially in the hips, neck, shoulders, and jaw. Incorporating somatic-inspired movements into your day can help release tension and encourage relaxation.
Simple Somatic Stretches
- Shoulder Rolls → Gently roll shoulders forward and backward 10 times.
- Hip Openers → Sit cross-legged and lean forward slightly to open hip muscles.
- Neck Releases → Slowly tilt your head side-to-side to release tightness.
- Cat-Cow Stretch → Get on all fours, arch your back (cow), and round it (cat) — repeat 8–10 times.
Why It Works
- Gentle stretching loosens muscle tension triggered by anxiety.
- Movement promotes the release of endorphins — your body’s natural “feel-good” chemicals.
- A 2018 review in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience suggests mindful movements reduce anxiety symptoms by improving interoceptive awareness — your ability to sense what’s happening inside your body (7).
Pro Tip
For maximum benefit, combine these techniques. For example:
- Start with body scanning to notice tension.
- Use diaphragmatic breathing to relax.
- End with gentle stretches to release stored energy.
Practicing these somatic techniques daily can train your nervous system to stay calmer under stress and respond more resiliently to anxiety triggers.
Somatic Psychotherapy: Healing Anxiety from the Inside Out
Unlike traditional therapies that primarily focus on thought patterns, somatic psychotherapy sees anxiety as a full-body experience. It works by:
- Recognizing how stress is stored in muscles and tissues
- Teaching the nervous system to complete incomplete stress cycles
- Combining talk therapy with movement, mindfulness, and breathwork
- Addressing both emotional and physical components of anxiety
According to research published in Frontiers in Psychology (2021), somatic-based interventions significantly reduce generalized anxiety symptoms and improve overall well-being (8).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’S)
1. How long does somatic therapy take to reduce anxiety?
A. It varies. Some people notice changes within a few sessions, while others require several weeks. Consistency and working with a trained therapist enhance results.
2. Can I practice somatic techniques on my own?
A. Yes. Simple practices like deep breathing, grounding, and gentle stretching can be done at home. However, deeper trauma-related anxiety benefits most from guided therapy.
3. Is somatic therapy scientifically proven for anxiety?
A. Yes. Several studies indicate that somatic therapies can reduce anxiety, PTSD, and chronic stress by helping the nervous system self-regulate and release stored tension.
Somatic therapy offers a holistic approach to healing anxiety by addressing not just thoughts and feelings but also the body’s response to stress. Through mindful awareness, gentle movement, and nervous system regulation, it helps individuals feel grounded, safe, and emotionally balanced.
If you struggle with anxiety that feels rooted in both mind and body, somatic therapy may be the missing link in your healing journey.