Important: This article is for informational purposes only. Please read our full disclaimer for more details.
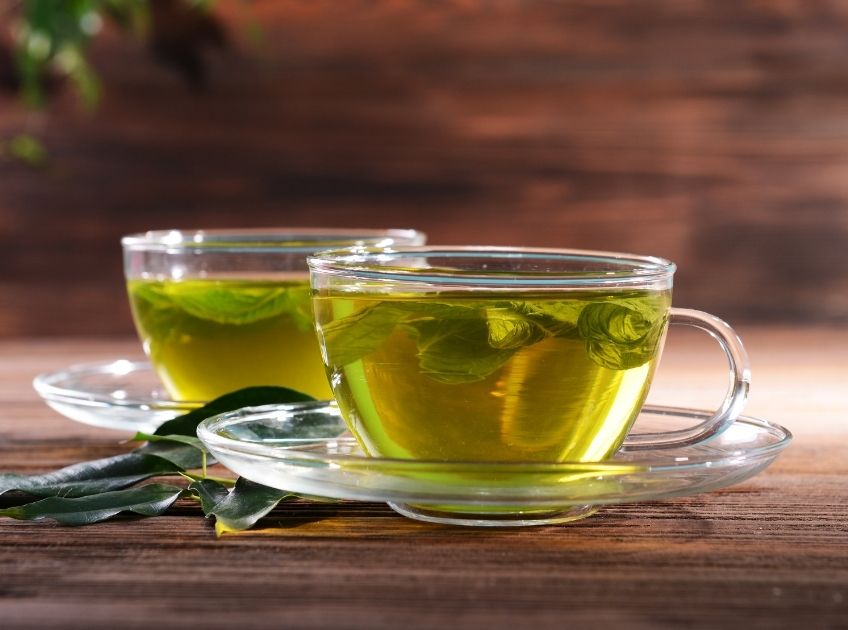
Bloating can strike anytime—after a heavy meal, during PMS, or when digestion slows down. For many, the first instinct is to reach for quick-relief tablets or home remedies. But what if a simple cup of green tea could help flatten that uncomfortable belly bloat? Known worldwide for its antioxidant and metabolism-boosting properties, green tea is increasingly being praised for its digestive benefits too. But does it actually work for bloating, or is it simply another wellness trend? Let’s break down the science.
Can Green Tea Really Reduce Bloating? Understanding How It Works
Green tea may be gentle, but it packs a powerful digestive punch. Here’s how it helps relieve bloating:
1. Rich in Antioxidants That Support Digestion
Green tea contains catechins, especially Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG), which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (1). When your gut is inflamed (due to poor diet, stress, or indigestion), bloating becomes more likely. The anti-inflammatory effects of catechins help soothe the digestive tract and support smoother digestion.
2. Helps Eliminate Gas and Ease Stomach Discomfort
One of the most common causes of bloating is the build-up of gas in the intestines. Green tea has natural carminative properties, helping to reduce gas formation and encourage its gentle release (2). This means less abdominal pressure, tightness, and discomfort.
3. A Natural Diuretic That Reduces Water Retention
Not all bloating is caused by gas—sometimes, it’s water retention. Green tea works as a natural diuretic, encouraging the body to eliminate excess water and sodium. This can lead to a visibly flatter tummy, especially for those who experience bloating due to hormonal fluctuations, high salt intake, or premenstrual symptoms.
4. Supports Gut Health and Healthy Gut Bacteria
Gut imbalance can cause fermentation, gas, and bloating. Some studies suggest that green tea polyphenols act as prebiotics, feeding good gut bacteria (3). A healthy gut microbiome means better digestion, less fermentation, and reduced bloating over time.
5. Helps Food Digest Faster
Green tea supports thermogenesis and metabolic activity, which means your digestive system works more efficiently (4). When food lingers in the gut, fermentation increases—leading to gas and heaviness. By stimulating digestion, green tea helps prevent this sluggishness and supports a lighter, more comfortable stomach.
How to Brew Green Tea for Bloating Relief (The Right Way)
Drinking green tea the right way matters. Steeping it incorrectly or drinking it at the wrong time can reduce its benefits or irritate the stomach.
Here’s how to prepare it for maximum digestive support:
1. Classic Green Tea for Digestion
Ingredients:
- 1 teaspoon high-quality green tea leaves (or 1 tea bag)
- 1 cup of hot water
Method:
- Heat water until warm—but not boiling (about 80–85°C). Boiling water makes green tea bitter and harsh on the stomach.
- Add tea leaves and steep for 2–3 minutes.
- Strain and sip warm.
2. Green Tea with Ginger for Faster Relief
- Ginger boosts digestive movement and eases gas.
- Add: 3–4 thin slices of fresh ginger while steeping.
3. Green Tea with Lemon for Reduced Bloating
- Lemon acts as a mild detoxifier and enhances green tea’s ability to reduce water retention.
- Add: 1 teaspoon fresh lemon juice just before drinking.
When Should You Drink It for Best Results?
- Drink 20–30 minutes after meals to support digestion.
- Avoid drinking green tea on an empty stomach as it may trigger acidity in some individuals.
- Limit to 2–3 cups daily to avoid caffeine-related discomfort.
What Science Says: Research Supporting Green Tea for Digestive Health
Studies suggest that green tea’s polyphenols can support gut health and digestion:
- A clinical review published in the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition highlighted that green tea catechins help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract and support healthy gut bacteria balance (3).
- Another study found that EGCG helps improve digestive efficiency and reduces symptoms of gastrointestinal discomfort, including bloating (1).
Together, these findings indicate that green tea is more than a traditional wellness beverage—it has research-backed digestive benefits that make it a helpful natural remedy for bloating.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’S)
1. How long does it take for green tea to reduce bloating?
A. Most people feel relief within 30–45 minutes, especially when consumed after meals. However, consistent daily intake offers the best long-term digestive benefits.
2. Can green tea cause bloating instead of helping it?
A. Yes, in some people, especially if consumed in excess or on an empty stomach. The caffeine and tannins may irritate the stomach lining, causing gas or acidity.
3. Is green tea better than herbal teas for bloating?
A. It depends. Green tea works well for digestion, water retention, and mild bloating. For severe gas or cramps, herbal teas like fennel, peppermint, or ginger may offer faster relief. Many people benefit from using both at different times.
So, does green tea help with bloating? Yes—green tea can be a natural and effective remedy for bloating caused by gas, inflammation, or water retention. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and digestive-boosting effects make it a gentle yet powerful addition to your daily routine.
Just remember: drink it warm, avoid over-steeping, and pair it with a balanced diet for best results. With regular use, green tea may help support better digestion, a calmer gut, and a lighter, more comfortable you.