Important: This article is for informational purposes only. Please read our full disclaimer for more details.
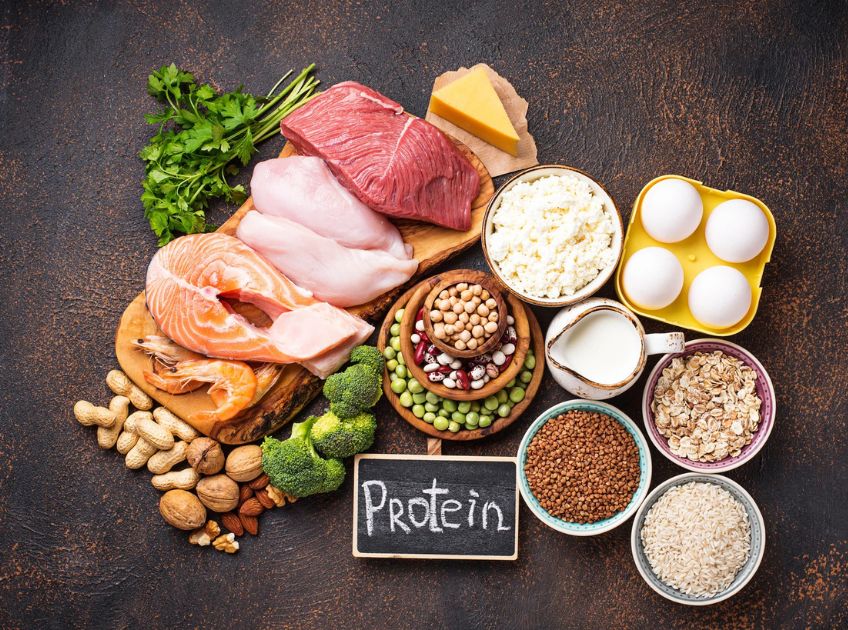
Protein is a vital macronutrient that plays a key role in building and repairing muscles, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting overall health. It is especially important for those who are physically active, recovering from illness, or aiming to maintain lean body mass. The body cannot store protein the way it stores carbohydrates or fat, which means consuming adequate amounts through your diet every day is essential.
Including high-protein foods in your meals can help you feel full, regulate blood sugar, and support metabolism. Additionally, research shows that protein-rich diets can enhance muscle synthesis, support bone health, and even improve cardiovascular wellness when paired with balanced nutrition (1).
15 High-Protein Foods You Should Include in Your Diet
1. Eggs
Eggs are a complete protein source, containing all nine essential amino acids. They also provide vitamins D, B12, and choline, which support brain health and metabolism.
Serving tip: Boil, scramble, or poach eggs. One large egg contains about 6 grams of protein.
2. Greek Yogurt
Greek yogurt has double the protein of regular yogurt, with 15–20 grams per cup. It also contains probiotics that aid digestion and calcium for bone health.
Serving tip: Mix with fresh berries or nuts for a protein-packed breakfast or snack.
3. Chicken Breast
Lean chicken breast is low in fat and high in protein, offering around 31 grams per 100 grams. It’s versatile for salads, sandwiches, and main dishes.
Serving tip: Grill, bake, or poach to preserve nutrients. Avoid breading or deep-frying.
4. Salmon
Salmon provides high-quality protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart and brain health. A 100-gram portion contains approximately 20 grams of protein.
Serving tip: Bake, grill, or steam salmon. Pair with vegetables for a balanced meal.
5. Cottage Cheese
Cottage cheese is rich in casein, a slow-digesting protein ideal for nighttime consumption. One cup provides around 25 grams of protein.
Serving tip: Eat plain, with fruit, or as a savory snack with herbs and spices.
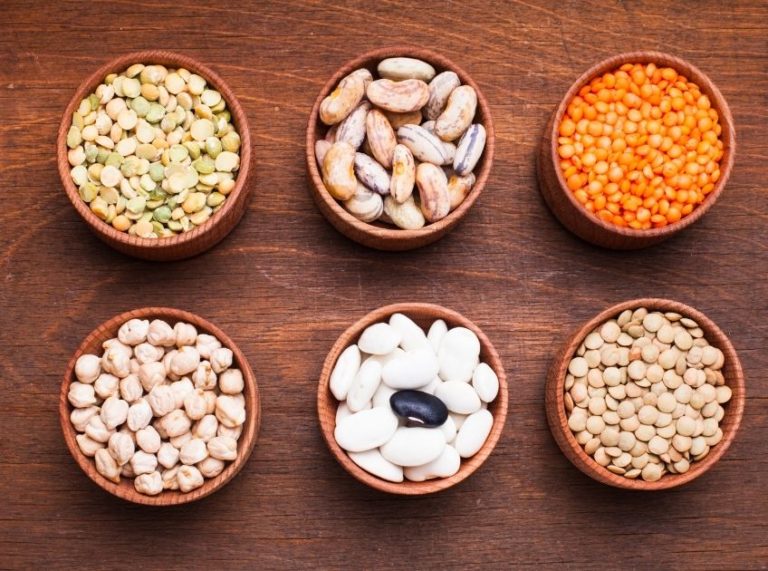
6. Lentils
Lentils are plant-based protein sources, offering about 18 grams per cooked cup. They also provide fiber, iron, and folate, supporting digestion and cardiovascular health.
Serving tip: Use in soups, stews, or salads. Combine with grains like rice or quinoa to create complete proteins.
7. Quinoa
Quinoa is a complete plant protein, containing all essential amino acids, with roughly 8 grams of protein per cooked cup. It also offers fiber, magnesium, and antioxidants.
Serving tip: Use as a base for salads, bowls, or as a rice substitute.
8. Almonds
Almonds provide 6 grams of protein per ounce (about 23 almonds). They are also rich in healthy fats, vitamin E, and magnesium, supporting skin and heart health.
Serving tip: Eat as a snack or sprinkle on oatmeal, yogurt, or salads.
9. Tofu
Tofu is made from soybeans and contains about 10 grams of protein per 100 grams. It’s also rich in calcium and iron, which are essential for bone and blood health.
Serving tip: Stir-fry, bake, or grill. Press before cooking for firmer texture.
10. Turkey
Lean turkey breast has around 29 grams of protein per 100 grams. It is low in fat and excellent for building lean muscle.
Serving tip: Add to sandwiches, salads, or as a main protein source in meals.
11. Black Beans
Black beans provide 15 grams of protein per cooked cup, along with fiber and antioxidants. They help regulate blood sugar and support gut health.
Serving tip: Include in soups, stews, or veggie burgers. Pair with whole grains for complete protein.
12. Shrimp
Shrimp is low in calories but high in protein, offering around 24 grams per 100 grams. It’s also a good source of selenium and vitamin B12.
Serving tip: Steam, grill, or sauté with vegetables. Avoid frying to keep it healthy.
13. Peanut Butter
Peanut butter contains 8 grams of protein per 2 tablespoons. It’s rich in healthy fats and antioxidants. Opt for natural, unsweetened varieties.
Serving tip: Spread on whole-grain bread, add to smoothies, or use as a dip for fruit.
14. Chia Seeds
Chia seeds provide 4 grams of protein per 2 tablespoons. They’re also packed with fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants.
Serving tip: Add to smoothies, oatmeal, or make chia pudding. Hydrate seeds before consumption for best digestion.
15. Beef
Lean cuts of beef provide 25–30 grams of protein per 100 grams. They also supply B vitamins, iron, and zinc, which support muscle growth and overall metabolism.
Serving tip: Choose lean cuts like sirloin or tenderloin. Grill, roast, or stir-fry for maximum nutrient retention.
The Science Behind High-Protein Diets
Studies show that protein is crucial for muscle synthesis, weight management, and overall metabolic health. According to research in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, diets high in protein can increase satiety, reduce overall calorie intake, and maintain lean muscle during weight loss (2). Plant-based proteins, like lentils and quinoa, offer additional fiber and phytonutrients, which have been linked to lower risks of heart disease and diabetes (3). Animal-based proteins, like chicken, fish, and eggs, provide complete amino acid profiles critical for tissue repair and growth (4).
For adults, general protein recommendations are around 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight per day, but those engaging in strength training or endurance activities may benefit from 1.2–2 grams per kilogram of body weight (5).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’S)
1. Can I get enough protein on a vegetarian or vegan diet?
A. Yes. Foods like lentils, quinoa, tofu, nuts, seeds, and beans provide sufficient protein when consumed in a balanced diet. Combining different plant-based proteins ensures you get all essential amino acids.
2. Are high-protein diets safe for the kidneys?
A. For healthy individuals, high-protein diets are generally safe. Those with pre-existing kidney disease should consult a doctor, as excessive protein may stress kidney function.
3. How can I add more protein to my meals without overloading on calories?
A. Choose lean protein sources like chicken, fish, tofu, and Greek yogurt. Incorporate beans, lentils, and nuts in moderation, and balance your diet with vegetables and whole grains.
Including high-protein foods in your diet is essential for overall health, muscle maintenance, and weight management. Animal and plant-based options, from eggs and chicken to lentils and quinoa, provide a variety of nutrients alongside protein. Understanding the science behind protein helps you make informed choices to support your fitness goals, metabolic health, and long-term well-being.
Recommended Topics:
- Best Protein Rich Foods for Picky Eaters
- 10 Protein High Foods for Vegetarians
- What’s Better Whey Protein Vs Plant-based Protein?
- The 10 Best Foods to Build Muscle
- How Much Time It Takes To Digest Eggs
- 10 Best Foods For Jaundice
- 10 Healthy Foods to Gain Weight Fast
- 10 Best Foods For An Upset Stomach
- 10 Best Foods for IBS Symptoms
- 7 Best Protein For Crepey Skin
- 10 Foods That Are High in Vitamin K2
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Tyrosine
- 10 Foods High in Fatty Acids
- 10 Foods That Contain Whey Protein
- 10 Foods That Boost Your Mental Health
- 10 Best Foods To Eat For Anemia
- 10 Best Healthy Fat Foods That You Should Eat
- 10 Foods That Are High in Nucleic Acid
- 10 Foods Are High in Nitrogen Add in Your Diet